Intelligent Writing Tutor
Contents
[hide]Intelligent Writing Tutor
Teruko Mitamura, Ruth Wylie, and Jim Rankin Project Advisors: Brian MacWhinney and Ken Koedinger
Abstract
As part of contributing to the PSLC's underlying goal of developing a theory of robust learning, the Intelligent Writing Tutor (IWT) project will explore the issue of transfer and long-term retention of acquired knowledge. We will look at positive, negative and null transfer from a student’s native language (L1), and their roles in learning and retaining information. We hope to be able to develop general principles that can then be applied to other domains.
Background
Research Motivation
We are interested in looking at the effects of transfer from L1 in language learning and English in particular. This study will contribute to the theory of robust learning by providing experimental data related to the often cited but little researched educational principle of “build on prior knowledge”. We hypothesize that elements of English that correspond to a student's L1 will be easier to learn than those elements that do not correspond (positive transfer). Moreover, elements for which there are no corresponding elements will be harder to learn (negative transfer). Our study will go beyond the simple Contrastive Analysis by examining at a detailed leveled the various features and their relative validity for a given knowledge component. For example, instead of looking at simply if articles exist in the native language, we will examine specific instances of article usage (e.g. immediate situation, general knowledge, sporadic reference, etc. (Sand, 2004)).
Educational Motivation
While error-free article use may not be necessary in order for most communication to occur (e.g. People usually understand what is meant by “Give me a book on the table” even when “Give me the book on the table” is correct), the problem becomes more severe when students submit written work, especially high-level work such as technical and academic reports. Errors in writing at this level may suggest, either consciously or unconsciously, that errors exist in the work itself (Master, 1997). Furthermore, students at this level are often aware of their difficulties with article use and are motivated to learn how to use articles correctly, thus developing a tutoring system that will help them develop better understanding and therefore produce error-free text and speech is likely to be well-received.
Research question
How is robust learning of English affected by L1 transfer?
Independent variables
Study 1:
The independent variable for this study is the student’s first language (L1). Students will be divided into groups based on the type of determiners present in their L1. Students with L1s do not have an article system (e.g. Chinese, Japanese, Korean) will be placed in one group, while students with L1s that do have an article system (e.g. Spanish, Arabic, French) will be placed in another.
Hypothesis
Study 1:
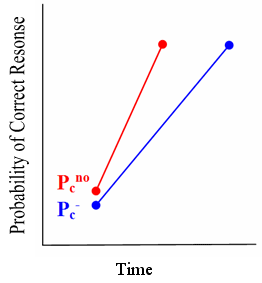
Hypothesis 1: Knowledge components subject to negative transfer will be harder to learn than knowledge components for which there is positive or no transfer
- Pcno – Probability of correct given no transfer
- Pc- – Probability of correct given negative transfer
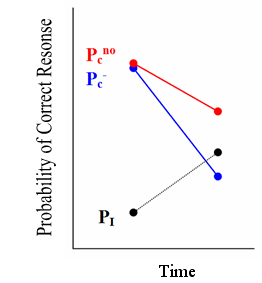
Hypothesis 2: Knowledge components subject to negative transfer will exhibit greater rate of decay than knowledge components for which there is positive or no transfer.
- Pcno – Probability of correct given no transfer
- Pc- – Probability of correct given negative transfer
- PI – Probability of Incorrect
Dependent variables
This study will utilize a series of post-tests which measure both normal and robust learning, including:
- Normal learning measures, immediate: Immediately following instruction, students will complete their first post-test in order to measure the effectiveness of the training itself. These tasks will be a measure of normal learning (near transfer, immediate testing).
- Normal learning measures, long-term retention: Additional post-tests will be administered 3, 10, 20, and 35 days after initial instruction. These measures will be similar to the ones students encountered during training but will assess the more robust learning measure of long-term retention.
- Transfer: In addition, we will collect student writing samples in order to determine if the instructional activities succeeded in enabling students to produce text with fewer errors.
Explanation
This study is part of the Fluency and Refinement cluster. The main hypothesis of this cluster is that the structure of instructional activities and student’s prior knowledge play critical roles in developing robust learning. Since students learning English are already fluent in at least one language, we can utilize this fact to better understand how a student’s prior knowledge affects acquisition of new knowledge components. The learning event space is described as follows:
Start
- Guess
- Entry is correct exit, with little learning
- Entry is incorrect Start
- Use the article of one’s first language
- Entry is correct exit, with possibly mistaken learning
- Entry is incorrect Start
- Try to apply knowledge of English article grammar
- Entry is correct Exit, with learning
- Entry is incorrect Start
The second set of paths (2, 2.1, 2.2) are only available to students whose first language has articles. Thus, this analysis is an instance of the explanation schema adding new paths.
Although this study seems on the surface to be a simple matter of measuring negative transfer, the learning events space analysis suggests that learning is contingent on students’ choices of paths. In particular, if the grammatical system of the first language is quite different from the English system, students may rapidly learn that choice 2 leads only to errors (2.2) so they may stop using their first language as the default solution. In that case, the expected negative transfer may not occur.
The study includes retention and acceleration of future learning measures. This allows testing of the so-called path independence hypothesis (Klahr & Nigam; Nokes & Ohlsson), which is that when students reach a certain level of competence, it doesn’t matter how they got there; their subsequent performance, including both retention and acceleration, will be the same. The PSLC theoretical framework suggests that the path to competence does make a difference, albeit a small one. If students make several errors per learning event, and thus have to cycle through the paths above several times, then when they do eventually produce the correct response, the encoding context is cluttered with features due to the errors and feedback messages. During testing, those features will be absent. Thus, students may be less able to retrieve the appropriate knowledge components. This predicts that students who make multiple errors during training, and this is likely to be the students who have path 2 available to them, are likely to have less robust learning.
Further Information
Results of the pilot study can be found here. [Need this link still]