Assistance Dilemma English Articles
| PI | Ruth Wylie, Teruko Mitamura, Ken Koedinger |
|---|---|
| Others with > 160 hours | Jim Rankin |
| Start date study 1 | September 2008 |
| End date study 1 | December 2008 |
| Start date study 2 | January 2008 |
| End date study 2 | May 2008 |
| Learnlab | English |
Contents
Intelligent Writing Tutor
Ruth Wylie, Teruko Mitamura, Ken Koedinger, and Jim Rankin
Abstract
This project focuses on integrated theory development with respect to the Assistance Dilemma (Koedinger and Aleven, 2007). A key goal is to have a theory that is sufficient to make a priori predictions about what instructional treatments yield the most robust learning.
The project focuses on exploring general principles of learning along two different dimensions of assistance: 1) task type: a) edit vs. b) selection; and 2) self-explanation: a) problems only vs. b) problems with prompts to self-explain. We instantiate these principles within the domain of the English article system and within the English as a Second Language LearnLab. In this domain, standard practice often uses the (a) values on the dimensions above (edit of multiple knowledge components with no self-explanation) whereas emerging PSLC theory and analysis predict that the (b) values on the dimensions (selection on a subset of knowledge components with self-explanation) will lead to greater robust learning outcomes. These dimensions are interesting for exploring a priori predictions as to whether adding difficulties (removing assistance) during instruction aids or harms eventual learning outcomes. For the task type dimension, our standing theoretical prediction is that the added demand of editing ahurt learning, while the added demand of self-explanation (dimension 2b) helps learning.
Study 1: Self-Explanation Study 1
Research Questions
Hypothesis
Since the added process of self-explanation is generative, students in the self-explanation with menu condition will show greater learning gains on both normal and robust learning measures than those in the practice-only condition and free-form self-explanation condition. We hypothesize that the added difficulty of generating explanations in the free-form condition is extraneous and thus will result in less learning than the menu-based self-explanation conditions.
Alternatively, generating self-explanations may require too much time and thus it may be better to provide students with extra examples and to implicitly learn the rules through the practice-only condition.
In addition, while self-explanation has proved to lead to greater learning in other domains, this would be the one of the first, if not the first, study to empirically examine its effects in second language grammar acquisition.
Independent Variables
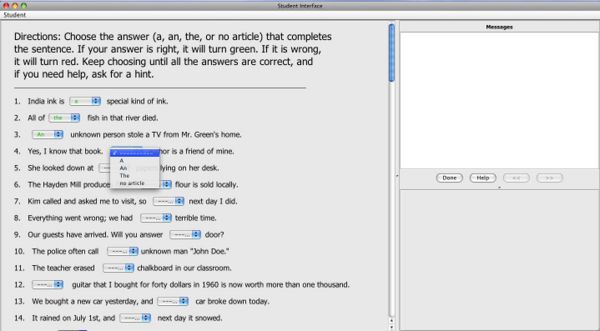
Image 1: Practice-Only Tutor - Using this tutor, students select an article (a, an, the, no article) from each sentence to complete the sentence.
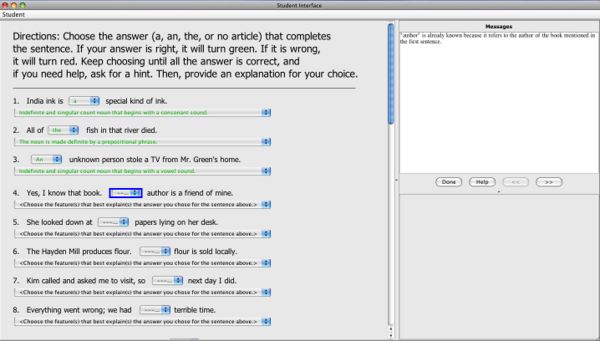
Image 2: Menu-based Self-Explanation Tutor - Using this tutor, students select an article (a, an, the, no article) from each sentence and choose the feature of the sentence that best explains the article choice.
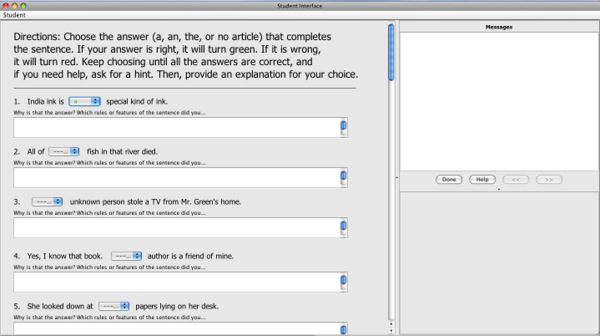
Image 3: Free-form Self-Explanation Tutor- Using this tutor, students select an article (a, an, the, no article) from each sentence and write an explanation for why they made their choice.
Dependent Variables
All students completed a computer-based pre and posttest that consisted of article-only and article with explanation items. In the article-only items, students chose an article from a dropdown menu to complete the sentence. In the article with explanation items, students chose an article to complete the sentence and then chose the feature or rule that explained their answer. No hints were available during the tests, and students did not receive feedback on their answers.
Results
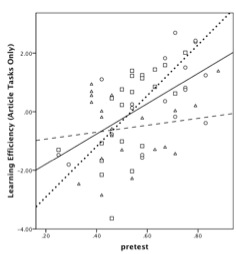
Students in all conditions showed significant pre to posttest improvement; however, there was no significant differences between conditions. Analysis using efficiency scores (a measure that combines learning gains and time-on-task into a single construct) revealed a significant aptitude by treatment interaction (F(2, 60) = 3.54, p = 0.036)
Study 2: Self Explanation Study 2
The second study, conducted in Spring 2009 in Levels 3, 4, and 5 of the English LearnLab compared a practice-only tutoring system to a worked examples with self-explanation system. The goal of this study was to further investigate the effects of self-explanation on second language grammar learning. In the self-explanation conditions in the previous study, students were required to select an article and select an explanation. In this study, we isolated the two tasks such that students were either selecting articles (practice-only) or selecting an exlanation (worked examples with self-explanation).
Independent Variables
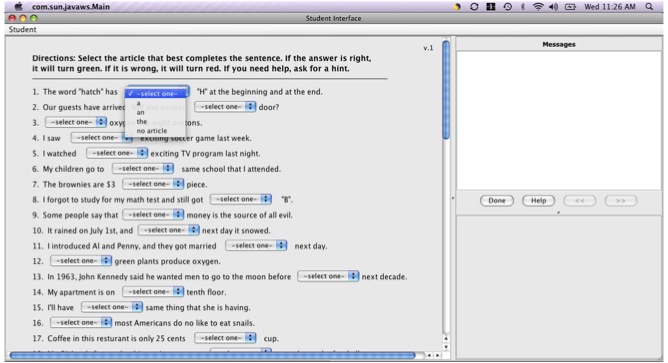
Practice-Only Tutor: Working with the practice-only tutor, students select an article (a, an, the, or no article) from a drop-down. Students receive immediate feedback on their selections and can request hints to help choose the right answer.
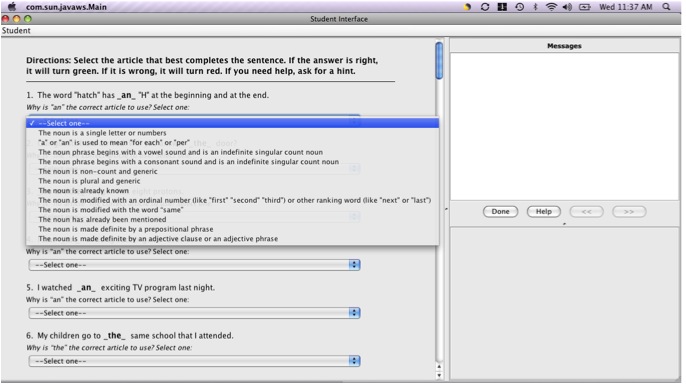
Worked Example with Self-Explanation Tutor:In the worked example plus self-explanation tutor, students are given a completed sentence with the target article highlighted and are asked to select the feature of the sentence that best explains the article choice.
Dependent Variables
Similar to Study 1, students were given a pretest and immediate posttest with items similar to those on which they were tutored. The pre and posttests contained both article selection and explanation selection items.
Results
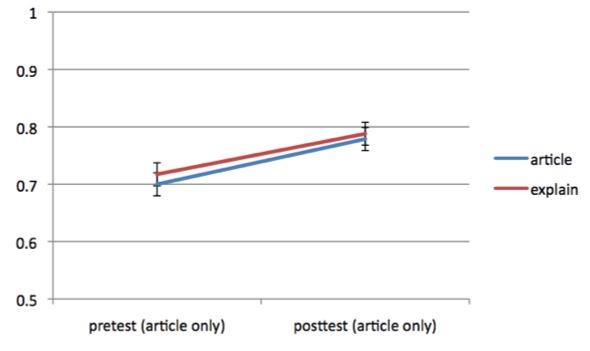
Results showed that students in both conditions showed significant learning gains (F(1, 99) = 40.28, p < 0.001) but there was no difference between conditions.
Contributions
These studies are the
References
1. Bjork, R. A. (1994). Memory and metamemory considerations in the training of human beings. In J. Metcalfe and A. Shimamura (Eds.), Metacognition: Knowing about knowing (pp.185-205). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
2. Celce-Murcia, Marianne, and Larsen-Freeman, Diane. (1983). The Grammar Book: An ESL/EFL Teacher’s Course. Rowley, Massachusetts: Newbury House Publishers.
3. Elson, Allegra B. Fossilized language forms: Implications and a search for solutions in an adult English as second language classroom. A PALPIN Inquiry Project, 2004.
4. Ericsson, K. A, & Simon, H. (1984). Protocol analysis: Verbal reports as data. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press
5. Hawkins, J. A. (1991). On (in) definite articles: implicatures and (un) grammaticality prediction. Journal of Linguistics(27), 405-442.
6. Knowledge Component Hypothesis (2007, April 30). In PSLC Theory Wiki. Retrieved March 27, 2008, from http://learnlab.org/research/wiki/index.php/Knowledge_component_hypothesis
7. Koedinger, K., & Aleven, V. (2007). Exploring the assistance dilemma in experiments with Cognitive Tutors. Educational Psychology Review. 19(3) 239-264.
8. Level 4 Writing Objectives. (2007, Novermber 13). Retrieved March 19, 2008, from http://learnlab.org/learnlabs/english/Level_4_Objectives/Objectives_Wr4fin.dco
9. Liu, D. & Gleason, J. (2002). Acquisition of the Article THE by Nonnative Speakers of English, An Analysis of Four Nongeneric Uses. SSLA, 24, 1-26.
10. Master, P. (1997). The English Article System: Acquisition, Function, and Pedagogy. System. 25,(2) 215-232.
11. Pavlik Jr., P.I., and Anderson, J. R. (2005). Practice and forgetting effects on vocabulary memory: An activation-based model of the spacing effect. Cognitive Science, 29(4), 559-586.
12. Schooler, JW & Engstler-Schooler, TY. (1990). Verbal overshadowing of visual memories: some things are better left unsaid. Cognitive Psychology. 22(1):36-71.
13. VanLehn, K., Siler, S., Murray, C., Yamauchi, T., & Baggett, W.B. (2003). Why do only some events cause learning during human tutoring? Cognition and Instruction, 21(3), 209-249.
14. Wylie, R. (2007) Are we asking the right questions? Understanding which tasks lead to the robust learning of English grammar. Accepted as a Young Researchers Track paper at the 13th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education. Marina del Rey, California. July 9 – 13, 2007.
15. Wylie, R. (2008) Putting a/the stake in the ground: Making a priori predictions of student learning. Accepted as a Young Researchers Track paper at Intelligent Tutoring Systems 2008. Montreal, Canada. June 23 – 27, 2008.