Difference between revisions of "Booth"
Julie-Booth (talk | contribs) (→Dependent Variables) |
(→References) |
||
| (97 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | == | + | ==Improving skill at solving equations through better encoding of algebraic concepts== |
Julie Booth, Robert Siegler, Ken Koedinger & Bethany Rittle-Johnson | Julie Booth, Robert Siegler, Ken Koedinger & Bethany Rittle-Johnson | ||
| + | |||
| + | *PI: Julie Booth | ||
| + | *Key faculty: Ken Koedinger, Robert Siegler, Bethany Rittle-Johnson | ||
| + | |||
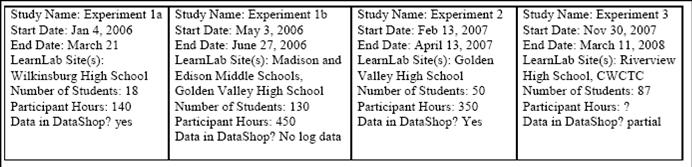
| + | *Studies: 4 complete | ||
| + | [[Image:StudyTable-Booth.jpg|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="5" style="text-align: left;" | ||
| + | |||
| + | | '''Exp 2 - Data available in DataShop''' || [https://pslcdatashop.web.cmu.edu/DatasetInfo?datasetId=149 Dataset: Corrective Self Explanation - 2006 (CTAT)]<br> | ||
| + | * '''Pre/Post Test Score Data:''' No | ||
| + | * '''Paper or Online Tests:''' Paper | ||
| + | * '''Scanned Paper Tests:''' No | ||
| + | * '''Blank Tests:''' No | ||
| + | * '''Answer Keys: ''' No | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''Exp 3 - Data available in DataShop''' || [https://pslcdatashop.web.cmu.edu/DatasetInfo?datasetId=196 Dataset: Self Explanation Riverview Fall 2007 (CTAT)] [https://pslcdatashop.web.cmu.edu/DatasetInfo?datasetId=293 Dataset: Self Explanation CWCTC Winter 2008 (CL)]<br> | ||
| + | * '''Pre/Post Test Score Data:''' No | ||
| + | * '''Paper or Online Tests:''' Paper | ||
| + | * '''Scanned Paper Tests:''' No | ||
| + | * '''Blank Tests:''' No | ||
| + | * '''Answer Keys: ''' No | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
===Abstract=== | ===Abstract=== | ||
| − | This project examines the effectiveness of corrective [[self-explanation]], or explanation of incorrect worked examples, for improving students' [[knowledge components]] for solving algebraic equations. Students in classrooms which are using the Algebra Cognitive Tutor curriculum will complete such exercises during their otherwise typical experience solving equations with the Tutor to determine whether coordination of the two instructional methods increases robust learning; as a control, other students in the classroom will receive typical self-explanation exercises (explanation of correct worked examples) or no self-explanation exercises amid their tutor problems. Robust learning will be assessed using measures of [[long-term retention]], [[transfer]], and [[accelerated future learning]]. | + | This project examines the effectiveness of corrective [[self-explanation]], or explanation of [[incorrect worked examples]], for improving students' [[knowledge components]] for solving algebraic equations. Students in classrooms which are using the Algebra Cognitive Tutor curriculum will complete such exercises during their otherwise typical experience solving equations with the Tutor to determine whether [[coordination]] of the two instructional methods increases [[robust learning]]; as a control, other students in the classroom will receive typical [[self-explanation]] exercises (explanation of correct worked examples) or no [[self-explanation]] exercises amid their tutor problems ([[Ecological control group]]). [[Robust learning]] will be assessed using measures of [[long-term retention]], [[transfer]], and [[accelerated future learning]]. |
===Glossary=== | ===Glossary=== | ||
*Corrective Self-Explanations: [[Self-explanation]]s of incorrect worked examples; explaining how and why they are incorrect | *Corrective Self-Explanations: [[Self-explanation]]s of incorrect worked examples; explaining how and why they are incorrect | ||
| − | *Incorrect worked examples: Examples that include errors | + | *Incorrect [[worked examples]]: Examples that include errors |
===Research Question=== | ===Research Question=== | ||
| − | Students tend to learn overgeneralized knowledge components and apply them when attempting to solve algebra problems with incorrect [[features]]. How can we help them to learn correct knowledge components? | + | Students tend to learn overgeneralized [[knowledge components]] and apply them when attempting to solve algebra problems with incorrect [[features]]. How can we help them to learn correct [[knowledge components]]? And when is combining exercises designed to improve [[conceptual knowledge]] with tutored [[procedural]] exercises effective for improving [[robust learning]] of algebraic problem-solving? |
===Background and Significance=== | ===Background and Significance=== | ||
| − | + | Errors are inevitable when individuals are first learning any skill; solving algebraic equations is no exception. Students often use incorrect [[knowledge components]] when learning Algebra (Lerch, 2004; Sebrechts, Enright, Bennett, & Martin, 1996), and use of incorrect [[knowledge components]] has been attributed to misunderstandings or gaps in students’ [[conceptual knowledge]] of Algebra (Anderson, 1989; Van Lehn & Jones, 1993). Results from Experiment 1 in Booth et al.’s current PSLC project confirm this hypothesis; a lack of knowledge about certain [[features]] in the problems (e.g., negatives, equals sign, like terms) was associated with use of related incorrect [[knowledge components]] on the problem-solving task. For example, students who do not see negatives as integral parts of terms in algebraic equations, or who believe that negatives can enter and exit equations without consequence tend to apply knowledge components with incorrect (or incomplete) [[features]] when solving equations, such as behaving in accordance with “to remove a term from an equation, subtract it from both sides” rather than with a [[knowledge component]] with [[feature validity]] that specifies “positive term” in the predicate, Thus, improving students’ knowledge of the conceptual [[features]] that underlie Algebra may be necessary for [[robust learning]] to occur. | |
| + | |||
| + | Siegler’s overlapping waves theory suggests that there are two important steps that are necessary to improve knowledge (Siegler, 1996): 1) Weaken the incorrect [[knowledge component]], and 2)Construct and strengthen correct [[knowledge component]]. One way to accomplish this is through [[self-explanation]], or generating explanations about instructional material. Chi and her colleagues (e.g., Chi, 2000; Roy & Chi, 2005) have shown that [[self-explanation]] is useful for a variety of purposes, including generating new knowledge to fill gaps and repairing faulty knowledge. Siegler (2002) suggests that one particular type of [[self-explanation]] may be especially useful for repairing faulty knowledge: explaining why the procedures used in [[incorrect worked examples]] are wrong. This [[self-explanation]] of [[incorrect worked examples]] (why they’re wrong) can weaken students’ overgeneralized [[knowledge components]] by helping them to understand both that the [[knowledge components]] are incorrect and what relevant [[features]] make them incorrect. | ||
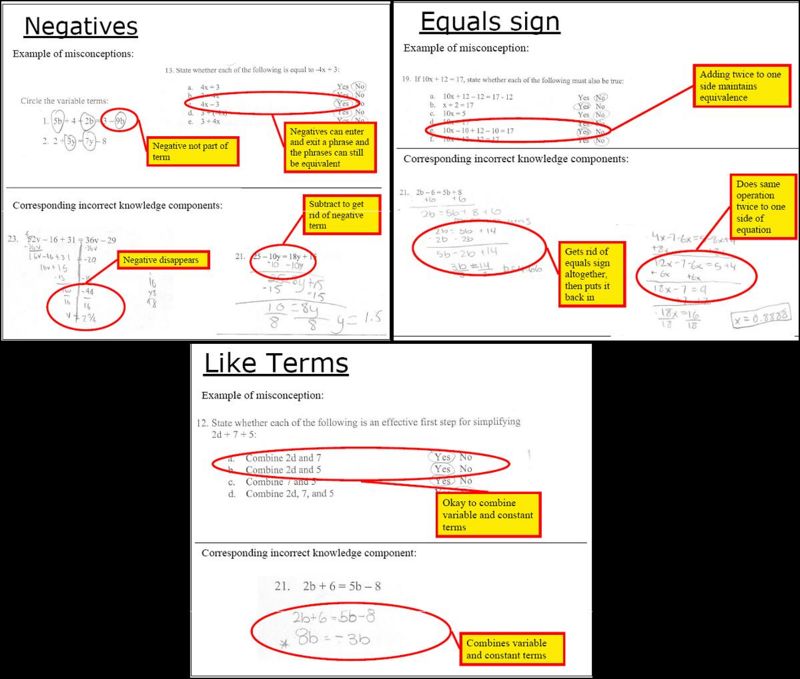
| − | + | Examples of corresponding misconceptions and incorrect knowledge components: | |
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:misconceptions2.jpg|800px]] | ||
===Dependent Variables=== | ===Dependent Variables=== | ||
| − | ''Normal | + | ''[[Normal post-test]]''. Near transfer—immediate posttest in which isomorphic problems to instruction are included for students to solve. (e.g., 3x + 10 = 20, 4x/3 + 4 = 16, 2/(-5x) = 14) |
| − | + | =====Robust Learning Measures:===== | |
| − | '' | + | ''[[Long-term retention]]''. Embedded assessment within instruction by the Cognitive Tutor. We will collect log data from the review portion of the next equation-solving Tutor unit to determine whether correct knowledge components are applied. |
| − | ''Accelerated | + | ''[[Transfer]]''. Problems included on the posttest in two forms: 1)Procedural format with more difficult problems/problems with additional features (e.g., 2x - 7 = -5x + 9, 4/(6x) – 7 = 32). 2) Conceptual format assessing knowledge of features (e.g., State whether each of the following is the same as 3 – 4x: a. 3 + 4x b. 3 + (-4x) c. 4x – 3 d. 4x + 3) |
| + | |||
| + | ''[[Accelerated future learning]]''. We will collect log data during tutor instruction in the next equation-solving Tutor unit when treatment is no longer in place to determine whether the slope of the learning curve is greater for students who received the [[corrective self-explanation]] treatment. | ||
===Independent Variables=== | ===Independent Variables=== | ||
| Line 35: | Line 66: | ||
Two types of self-explanation exercises: | Two types of self-explanation exercises: | ||
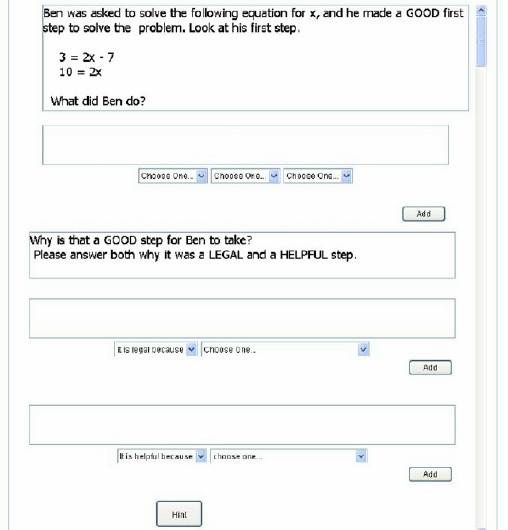
| − | 1) Typical self-explanation (explanation of correct worked examples) | + | 1) Typical self-explanation (explanation of correct [[worked examples]]) |
[[Image:TSE2.jpg]] | [[Image:TSE2.jpg]] | ||
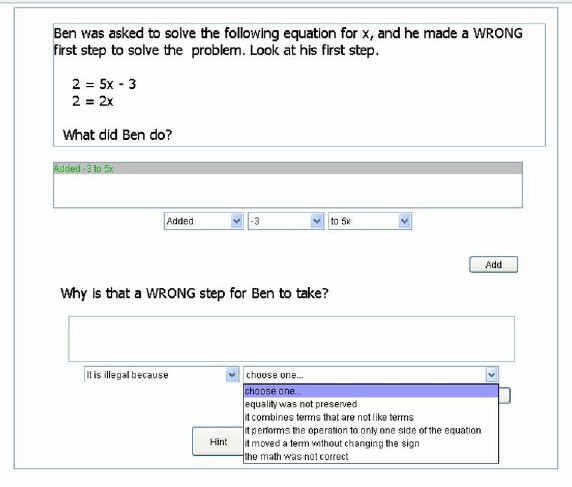
| − | 2) Corrective self-explanation (explanation of incorrect worked examples) | + | 2) [[Corrective self-explanation]] (explanation of [[incorrect worked examples]]) |
[[Image:CSE3.jpg]] | [[Image:CSE3.jpg]] | ||
| − | The design is a 2 x 2 | + | The design is a 2 x 2 factorial with two levels of typical self-explanation (yes or no) and two levels of [[corrective self-explanation]] (yes and no). The result is that within any participating classroom, one fourth of students received typical self-explanation, one fourth received [[corrective self-explanation]], one fourth received both, and one fourth received neither (the current tutor as-is, the [[Ecological control group]]. |
| + | |||
| + | ===Hypothesis=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Self-explanation]] of [[incorrect worked examples]] (why they’re wrong) combined with [[procedural]] practice can lead to [[robust learning]] through two processes: 1) Weaken low-[[feature validity]] [[knowledge components]] (know that they’re wrong and why they’re wrong) 2) Facilitate construction of high-[[feature validity]] [[knowledge components]]. See [[Corrective self-explanation]] (relevant instructional principle) | ||
| − | + | ===Findings=== | |
| − | === | + | =====Findings for Experiments 1a and 1b:===== |
| − | + | *Pretest misconceptions about [[features]] are related to use of specific incorrect [[knowledge components]] to solve problems Concepts related to specific buggy procedures | |
| + | **Students with incorrect or missing equality or terms [[features]] are more likely to make errors of those types (p’s < .05 and .01); nonsignificant trend in the same direction for negative feature | ||
| + | *Having knowledge of the [[features]] of negativity and equality predicts correctness on [[procedural]] problems (p’s < .05 and .01) | ||
| + | *Students do improve from pretest to posttest, but roughly 1/3 of students still lack each of the [[features]] at posttest | ||
| + | *Pretest [[conceptual knowledge]] predicts students' pretest to posttest gain in [[procedural]] knowledge after using the Algebra Tutor as is | ||
| + | *Improvement in [[conceptual knowledge]] of the equals sign feature leads to more learning on the [[procedural]] problems than if that knowledge was not improved. | ||
| − | === | + | =====Findings from Experiments 2 and 3:===== |
| − | Students who | + | *Students who received any kind of [[self-explanation]] exercises show greater learning of procedural [[knowledge components]] for solving algebraic equations compared with students who did not get any type of [[self-explanation]] exercises ([[Ecological control group]]). (Booth, 2009; Booth, Koedinger, & Siegler, 2008) |
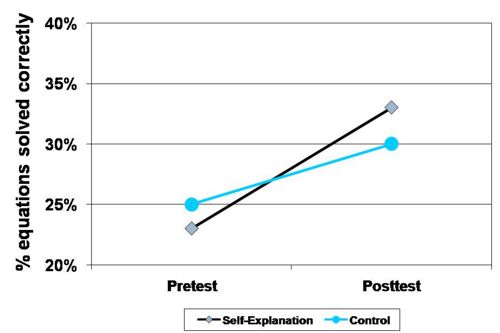
| + | **Improved the number of problems solved by 10%, while control group improved by 5%. No significant differnence, but experimental group students did at least as well as the control students, even though they had less practice solving problems. | ||
| + | [[Image:procedural.jpg|500px]] | ||
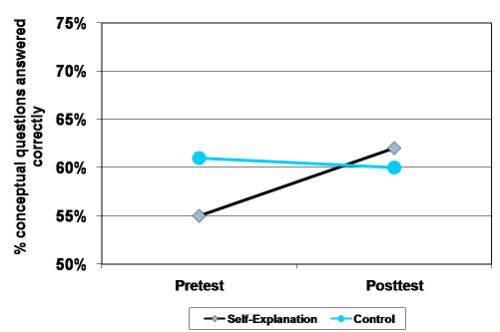
| + | **Improved their percent of conceptual questions answered correctly by 7% (control group ''decreased'' by 1%; p < .05) | ||
| + | [[Image:conceptual.jpg|500px]] | ||
| + | *Recieving [[Corrective self-explanation]] exercises leads to greater improvement in released items from standardized achievement tests. | ||
| + | *[[Corrective self-explanation]] may affect students differently based on the amount and quality of their [[knowledge components]] prior to beginning the treatment. | ||
| + | **Students with low and medium-level conceptual knowledge at pretest tend to perform better with [[corrective self-explanation]] than [[typical self-explanation]] | ||
| + | **Students with high conceptual knowledge at pretest perform better with [[typical self-explanation]] than [[corrective self-explanation]]. | ||
===Explanation=== | ===Explanation=== | ||
| − | Students who receive corrective self-explanation exercises are expected to gain improved explicit | + | Students who receive [[corrective self-explanation]] exercises are expected to gain improved explicit [[conceptual knowledge]] about the [[features]] in problems that make certain [[knowledge components]] inappropriate. This expected to lead to greater [[robust learning]] compared with the other conditions that gain only implicit knowledge or explicit knowledge but do not have this additional knowledge about when it is appropriate to apply their [[knowledge components]]. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Descendents=== | ===Descendents=== | ||
| Line 65: | Line 111: | ||
None | None | ||
| − | === | + | === Presentations/Publications=== |
| + | *Booth, J.L. (2009). Improving Algebra Learning in Real World Classrooms with Worked Examples and Self-Explanation. Paper presented at the Presidential Symposium entitled The New Learning Sciences at the annual meeting of the Eastern Psychological Association, Pittsburgh, PA, March 5-8, 2009. | ||
| + | *Booth, J.L., & Koedinger, K.R. (2008). Key misconceptions in algebraic problem solving. In B.C. Love, K. McRae, & V. M. Sloutsky (Eds.), Proceedings of the 30th Annual Cognitive Science Society (pp. 571-576). Austin, TX: Cognitive Science Society. | ||
| + | *Booth, J.L., Koedinger, K.R., & Siegler, R.S. (2008, July). Using self-explanation to improve algebra learning. Poster presented at the 30th annual meeting of the Cognitive Science Society, Washington, D.C. | ||
| + | *Booth, J.L., Koedinger, K.R., & Siegler, R.S. (2007a). The effect of prior conceptual knowledge on procedural performance and learning in algebra. Poster presented at the 29th Annual Cognitive Science Society conference in Nashville, TN. [http://www.learnlab.org/uploads/mypslc/publications/ma206-booth.pdf Abstract] | ||
| + | *Booth, J.L., Koedinger, K., & Siegler, R.S. (2007b). The effect of corrective and typical self-explanation on algebraic problem solving. Poster presented at the Science of Learning Centers Awardee’s Meeting in Washington, DC, October, 2007. | ||
*Presentation to the PSLC Advisory Board, Fall 2006. [http://www.learnlab.org/uploads/mypslc/talks/booth%202006%20advisory%20board%20talk%20slides.ppt Link to Powerpoint slides] | *Presentation to the PSLC Advisory Board, Fall 2006. [http://www.learnlab.org/uploads/mypslc/talks/booth%202006%20advisory%20board%20talk%20slides.ppt Link to Powerpoint slides] | ||
| − | === | + | ===References=== |
| + | |||
| + | Anderson, J.R. (1989). The analogical origins of errors in problem solving. In D. Klahr & K. Kotovsky (Eds). Complex information processing: The impact of Herbert A. Simon. (pp. 343-371). Hillsdale, NJ, England: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Chi, M.T.H. (2000) Self-explaining expository texts: The dual processes of generating inferences and repairing mental models. In Glaser, R. (Ed.) Advances in Insturctional Psychology, Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, pp. 161-238. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Lerch, C. M. (2004). Control decisions and personal beliefs: Their effect on solving mathematical problems. Journal of Mathematical Behavior, 23, 21-36. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Roy, M. & Chi, M.T.H. (2005). Self-explanation in a multi-media context. In R. Mayer (Ed.), Cambridge Handbook of Multimedia Learning (pp. 271-286). Cambridge Press. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Siegler, R.S. (1996). Emerging minds: The process of change in children’s thinking. New York: Oxford University Press. | ||
Siegler, R. S. (2002). Microgenetic studies of self-explanations. In N. Granott & J. Parziale (Eds.), Microdevelopment: Transition processes in development and learning (pp. 31-58). New York: Cambridge University. | Siegler, R. S. (2002). Microgenetic studies of self-explanations. In N. Granott & J. Parziale (Eds.), Microdevelopment: Transition processes in development and learning (pp. 31-58). New York: Cambridge University. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Van Lehn, K., & Jones, R.M. (1993). What mediates the self-explanation effect? Knowledge gaps, schemas, or analogies? In M. Polson (Ed.) Proceedings of the Fifteenth Annual Conference of the Cognitive Science Society (pp. 1034-1039). | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Data available in DataShop]] | ||
Latest revision as of 20:16, 15 December 2010
Contents
- 1 Improving skill at solving equations through better encoding of algebraic concepts
Improving skill at solving equations through better encoding of algebraic concepts
Julie Booth, Robert Siegler, Ken Koedinger & Bethany Rittle-Johnson
- PI: Julie Booth
- Key faculty: Ken Koedinger, Robert Siegler, Bethany Rittle-Johnson
- Studies: 4 complete
| Exp 2 - Data available in DataShop | Dataset: Corrective Self Explanation - 2006 (CTAT)
|
| Exp 3 - Data available in DataShop | Dataset: Self Explanation Riverview Fall 2007 (CTAT) Dataset: Self Explanation CWCTC Winter 2008 (CL)
|
Abstract
This project examines the effectiveness of corrective self-explanation, or explanation of incorrect worked examples, for improving students' knowledge components for solving algebraic equations. Students in classrooms which are using the Algebra Cognitive Tutor curriculum will complete such exercises during their otherwise typical experience solving equations with the Tutor to determine whether coordination of the two instructional methods increases robust learning; as a control, other students in the classroom will receive typical self-explanation exercises (explanation of correct worked examples) or no self-explanation exercises amid their tutor problems (Ecological control group). Robust learning will be assessed using measures of long-term retention, transfer, and accelerated future learning.
Glossary
- Corrective Self-Explanations: Self-explanations of incorrect worked examples; explaining how and why they are incorrect
- Incorrect worked examples: Examples that include errors
Research Question
Students tend to learn overgeneralized knowledge components and apply them when attempting to solve algebra problems with incorrect features. How can we help them to learn correct knowledge components? And when is combining exercises designed to improve conceptual knowledge with tutored procedural exercises effective for improving robust learning of algebraic problem-solving?
Background and Significance
Errors are inevitable when individuals are first learning any skill; solving algebraic equations is no exception. Students often use incorrect knowledge components when learning Algebra (Lerch, 2004; Sebrechts, Enright, Bennett, & Martin, 1996), and use of incorrect knowledge components has been attributed to misunderstandings or gaps in students’ conceptual knowledge of Algebra (Anderson, 1989; Van Lehn & Jones, 1993). Results from Experiment 1 in Booth et al.’s current PSLC project confirm this hypothesis; a lack of knowledge about certain features in the problems (e.g., negatives, equals sign, like terms) was associated with use of related incorrect knowledge components on the problem-solving task. For example, students who do not see negatives as integral parts of terms in algebraic equations, or who believe that negatives can enter and exit equations without consequence tend to apply knowledge components with incorrect (or incomplete) features when solving equations, such as behaving in accordance with “to remove a term from an equation, subtract it from both sides” rather than with a knowledge component with feature validity that specifies “positive term” in the predicate, Thus, improving students’ knowledge of the conceptual features that underlie Algebra may be necessary for robust learning to occur.
Siegler’s overlapping waves theory suggests that there are two important steps that are necessary to improve knowledge (Siegler, 1996): 1) Weaken the incorrect knowledge component, and 2)Construct and strengthen correct knowledge component. One way to accomplish this is through self-explanation, or generating explanations about instructional material. Chi and her colleagues (e.g., Chi, 2000; Roy & Chi, 2005) have shown that self-explanation is useful for a variety of purposes, including generating new knowledge to fill gaps and repairing faulty knowledge. Siegler (2002) suggests that one particular type of self-explanation may be especially useful for repairing faulty knowledge: explaining why the procedures used in incorrect worked examples are wrong. This self-explanation of incorrect worked examples (why they’re wrong) can weaken students’ overgeneralized knowledge components by helping them to understand both that the knowledge components are incorrect and what relevant features make them incorrect.
Examples of corresponding misconceptions and incorrect knowledge components:
Dependent Variables
Normal post-test. Near transfer—immediate posttest in which isomorphic problems to instruction are included for students to solve. (e.g., 3x + 10 = 20, 4x/3 + 4 = 16, 2/(-5x) = 14)
Robust Learning Measures:
Long-term retention. Embedded assessment within instruction by the Cognitive Tutor. We will collect log data from the review portion of the next equation-solving Tutor unit to determine whether correct knowledge components are applied.
Transfer. Problems included on the posttest in two forms: 1)Procedural format with more difficult problems/problems with additional features (e.g., 2x - 7 = -5x + 9, 4/(6x) – 7 = 32). 2) Conceptual format assessing knowledge of features (e.g., State whether each of the following is the same as 3 – 4x: a. 3 + 4x b. 3 + (-4x) c. 4x – 3 d. 4x + 3)
Accelerated future learning. We will collect log data during tutor instruction in the next equation-solving Tutor unit when treatment is no longer in place to determine whether the slope of the learning curve is greater for students who received the corrective self-explanation treatment.
Independent Variables
Two types of self-explanation exercises:
1) Typical self-explanation (explanation of correct worked examples)
2) Corrective self-explanation (explanation of incorrect worked examples)
The design is a 2 x 2 factorial with two levels of typical self-explanation (yes or no) and two levels of corrective self-explanation (yes and no). The result is that within any participating classroom, one fourth of students received typical self-explanation, one fourth received corrective self-explanation, one fourth received both, and one fourth received neither (the current tutor as-is, the Ecological control group.
Hypothesis
Self-explanation of incorrect worked examples (why they’re wrong) combined with procedural practice can lead to robust learning through two processes: 1) Weaken low-feature validity knowledge components (know that they’re wrong and why they’re wrong) 2) Facilitate construction of high-feature validity knowledge components. See Corrective self-explanation (relevant instructional principle)
Findings
Findings for Experiments 1a and 1b:
- Pretest misconceptions about features are related to use of specific incorrect knowledge components to solve problems Concepts related to specific buggy procedures
- Students with incorrect or missing equality or terms features are more likely to make errors of those types (p’s < .05 and .01); nonsignificant trend in the same direction for negative feature
- Having knowledge of the features of negativity and equality predicts correctness on procedural problems (p’s < .05 and .01)
- Students do improve from pretest to posttest, but roughly 1/3 of students still lack each of the features at posttest
- Pretest conceptual knowledge predicts students' pretest to posttest gain in procedural knowledge after using the Algebra Tutor as is
- Improvement in conceptual knowledge of the equals sign feature leads to more learning on the procedural problems than if that knowledge was not improved.
Findings from Experiments 2 and 3:
- Students who received any kind of self-explanation exercises show greater learning of procedural knowledge components for solving algebraic equations compared with students who did not get any type of self-explanation exercises (Ecological control group). (Booth, 2009; Booth, Koedinger, & Siegler, 2008)
- Improved the number of problems solved by 10%, while control group improved by 5%. No significant differnence, but experimental group students did at least as well as the control students, even though they had less practice solving problems.
- Improved their percent of conceptual questions answered correctly by 7% (control group decreased by 1%; p < .05)
- Recieving Corrective self-explanation exercises leads to greater improvement in released items from standardized achievement tests.
- Corrective self-explanation may affect students differently based on the amount and quality of their knowledge components prior to beginning the treatment.
- Students with low and medium-level conceptual knowledge at pretest tend to perform better with corrective self-explanation than typical self-explanation
- Students with high conceptual knowledge at pretest perform better with typical self-explanation than corrective self-explanation.
Explanation
Students who receive corrective self-explanation exercises are expected to gain improved explicit conceptual knowledge about the features in problems that make certain knowledge components inappropriate. This expected to lead to greater robust learning compared with the other conditions that gain only implicit knowledge or explicit knowledge but do not have this additional knowledge about when it is appropriate to apply their knowledge components.
Descendents
None
Presentations/Publications
- Booth, J.L. (2009). Improving Algebra Learning in Real World Classrooms with Worked Examples and Self-Explanation. Paper presented at the Presidential Symposium entitled The New Learning Sciences at the annual meeting of the Eastern Psychological Association, Pittsburgh, PA, March 5-8, 2009.
- Booth, J.L., & Koedinger, K.R. (2008). Key misconceptions in algebraic problem solving. In B.C. Love, K. McRae, & V. M. Sloutsky (Eds.), Proceedings of the 30th Annual Cognitive Science Society (pp. 571-576). Austin, TX: Cognitive Science Society.
- Booth, J.L., Koedinger, K.R., & Siegler, R.S. (2008, July). Using self-explanation to improve algebra learning. Poster presented at the 30th annual meeting of the Cognitive Science Society, Washington, D.C.
- Booth, J.L., Koedinger, K.R., & Siegler, R.S. (2007a). The effect of prior conceptual knowledge on procedural performance and learning in algebra. Poster presented at the 29th Annual Cognitive Science Society conference in Nashville, TN. Abstract
- Booth, J.L., Koedinger, K., & Siegler, R.S. (2007b). The effect of corrective and typical self-explanation on algebraic problem solving. Poster presented at the Science of Learning Centers Awardee’s Meeting in Washington, DC, October, 2007.
- Presentation to the PSLC Advisory Board, Fall 2006. Link to Powerpoint slides
References
Anderson, J.R. (1989). The analogical origins of errors in problem solving. In D. Klahr & K. Kotovsky (Eds). Complex information processing: The impact of Herbert A. Simon. (pp. 343-371). Hillsdale, NJ, England: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc.
Chi, M.T.H. (2000) Self-explaining expository texts: The dual processes of generating inferences and repairing mental models. In Glaser, R. (Ed.) Advances in Insturctional Psychology, Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, pp. 161-238.
Lerch, C. M. (2004). Control decisions and personal beliefs: Their effect on solving mathematical problems. Journal of Mathematical Behavior, 23, 21-36.
Roy, M. & Chi, M.T.H. (2005). Self-explanation in a multi-media context. In R. Mayer (Ed.), Cambridge Handbook of Multimedia Learning (pp. 271-286). Cambridge Press.
Siegler, R.S. (1996). Emerging minds: The process of change in children’s thinking. New York: Oxford University Press.
Siegler, R. S. (2002). Microgenetic studies of self-explanations. In N. Granott & J. Parziale (Eds.), Microdevelopment: Transition processes in development and learning (pp. 31-58). New York: Cambridge University.
Van Lehn, K., & Jones, R.M. (1993). What mediates the self-explanation effect? Knowledge gaps, schemas, or analogies? In M. Polson (Ed.) Proceedings of the Fifteenth Annual Conference of the Cognitive Science Society (pp. 1034-1039).