Difference between revisions of "Gifted"
(→Motivation as a Central role in Giftedness) |
(→Motivation as Facilitating Giftedness) |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
===Motivation as Facilitating Giftedness=== | ===Motivation as Facilitating Giftedness=== | ||
[[Image:Gagne, 2000.jpg|thumb|Gagne (2000) Ten Commandments for Academic Talent Development]] | [[Image:Gagne, 2000.jpg|thumb|Gagne (2000) Ten Commandments for Academic Talent Development]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | Considered the traditional approach to giftedness, this theory looks at the ability of the gifted individual as playing the largest role in the development of gifted behavior. A popular model for this theory is the Differentiated Models of Giftedness and Talent (DMGT). Proposed by Francoys Gange, this model places a distinction between gift and later talent. Natural ability or gift is the inherited ability of the person, and can be intellectual, creative, socioaffective or sensory motor. Talent is the how, through a series of affecters, this gift is expressed. The talent may be in a variety of areas, such as academics, the arts, or sports. | |
| − | + | Among the traditional views, this can be considered an advanced one. Where older knowledge saw raw gift as the sole measure for later talent, this model sees various affecters as | |
| + | One of the affecters that aids the development of talent is motivation (cited as an interpersonal catalyst). Though this view is a considerable step from the older views of giftedness playing a role in the development of natural ability into later talent. | ||
===Motivation as a Central role in Giftedness=== | ===Motivation as a Central role in Giftedness=== | ||
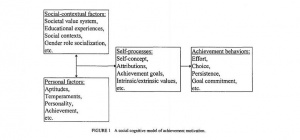
[[Image:Dai, Moon, Feldhusen (1998).jpg|thumb|Socio-Contextual Model]] | [[Image:Dai, Moon, Feldhusen (1998).jpg|thumb|Socio-Contextual Model]] | ||
Revision as of 09:18, 26 March 2009
This page is reserved for work on the topic of intellectual giftedness and motivation.
Giftedness or Intellectual Giftedness is characterized by intellectual development in children that surpasses those of their same age. Gifted children often show greater ability at grasping harder academic concepts and at times greater creativity than those of their same grade level.
Contents
Measuring Intellectual Giftedness
Though all measures of giftedness attempt to classify students with intellectual ability higher than their peers, it continues to be heavily debated. In the United States public school system the classification of gifted individuals is reffered to as:
a child or youth who performs at or shows the potential for performing at a remarkably high level of accomplishment when compared to others of the same age, experience or environment and who:
1) exhibits high performance capability in an intellectual, creative, or artistic area
2) possesses and unusual capacity for leadership or
3) excels in a specific academic field
(74th legislature of the State of Texas, Chapter 29, Subchapter D, Section 29.121) Identifying Gifted Students
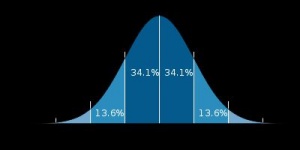
Yet even if the US public school identifies various factors as playing a part in giftedness, the IQ test is still considered to be the central tool in diagnosing giftedness. This is due to its consistency and high level of development, which allows for a particular student's scores to be measures against a very large sample's score.
Within studies that use IQ tests, the The common cutoff for giftedness is one standard deviation above the mean, or 84th percentile and above.
Giftedness and Motivation
The split in the role of motivation and giftedness is between those that theorize giftedness as being a mixture of talent and motivation and those that theorize giftedness as innate talent.
Motivation as Facilitating Giftedness
Considered the traditional approach to giftedness, this theory looks at the ability of the gifted individual as playing the largest role in the development of gifted behavior. A popular model for this theory is the Differentiated Models of Giftedness and Talent (DMGT). Proposed by Francoys Gange, this model places a distinction between gift and later talent. Natural ability or gift is the inherited ability of the person, and can be intellectual, creative, socioaffective or sensory motor. Talent is the how, through a series of affecters, this gift is expressed. The talent may be in a variety of areas, such as academics, the arts, or sports.
Among the traditional views, this can be considered an advanced one. Where older knowledge saw raw gift as the sole measure for later talent, this model sees various affecters as One of the affecters that aids the development of talent is motivation (cited as an interpersonal catalyst). Though this view is a considerable step from the older views of giftedness playing a role in the development of natural ability into later talent.